Energy efficiency sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality. From strategies in buildings to renewable energy sources, this guide delves deep into the world of efficient energy use.
Energy Efficiency in Buildings
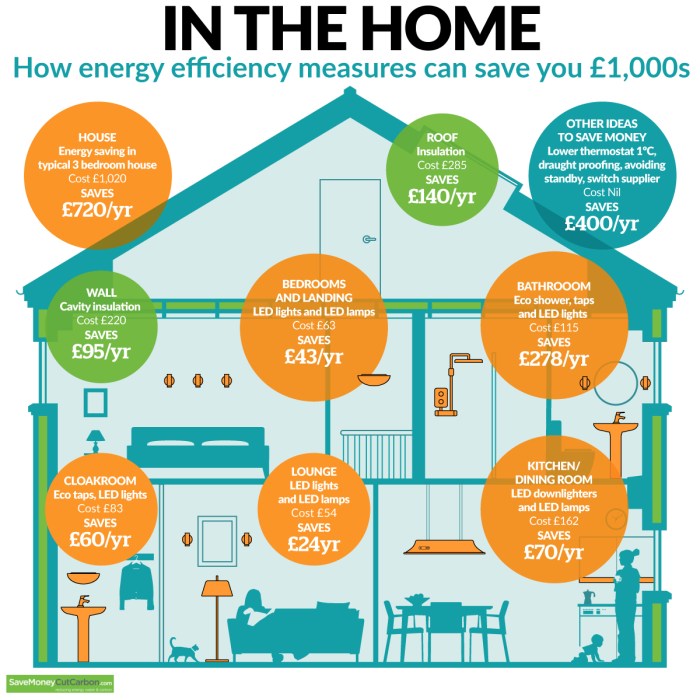
Energy efficiency in buildings refers to the utilization of less energy to achieve the same level of comfort, functionality, and productivity. It involves implementing measures to reduce energy consumption while maintaining or improving the performance of the building.
Strategies for Improving Energy Efficiency
- Proper Insulation: Ensuring that walls, roofs, and floors are well-insulated can prevent heat loss in the winter and keep cool air inside during the summer, reducing the need for heating and cooling.
- Energy-Efficient Windows: Installing windows with double or triple glazing and low-emissivity coatings can minimize heat transfer, improve insulation, and reduce the reliance on artificial heating and cooling systems.
- Efficient Lighting: Using LED or CFL bulbs instead of incandescent ones, implementing daylighting strategies, and installing sensors and timers can significantly lower electricity consumption for lighting purposes.
The Role of Insulation, Windows, and Lighting
Insulation, windows, and lighting play crucial roles in enhancing energy efficiency in buildings. Proper insulation helps in maintaining a consistent indoor temperature, reducing the workload on heating and cooling systems. Energy-efficient windows prevent heat loss or gain, contributing to lower energy usage.
Additionally, efficient lighting solutions not only reduce electricity consumption but also create a more comfortable and sustainable environment.
Energy-Efficient Appliances

Energy-efficient appliances are designed to consume less energy while still providing the same level of performance as standard appliances. They are built with advanced technologies that reduce energy waste and help lower electricity bills.When comparing energy consumption between standard and energy-efficient appliances, the difference can be significant.
Energy-efficient appliances can consume up to 50% less energy than their standard counterparts, making them a cost-effective choice in the long run.
Refrigerators
Energy-efficient refrigerators are equipped with features like improved insulation, energy-saving compressors, and smart temperature controls. These appliances help reduce energy consumption and keep food fresh while lowering electricity costs.
Washing Machines
Energy-efficient washing machines use less water and electricity per cycle compared to standard models. They often have advanced settings for water levels, temperature control, and faster spin cycles, resulting in lower energy consumption and reduced water usage.
LED Light Bulbs
LED light bulbs are energy-efficient lighting options that consume less electricity and have a longer lifespan than traditional incandescent bulbs. They provide bright illumination while reducing energy costs and the frequency of bulb replacements.
Dishwashers
Energy-efficient dishwashers use less water and energy during each wash cycle. They are designed with features like soil sensors, efficient spray arms, and eco-friendly wash cycles to optimize performance while minimizing energy waste.
Renewable Energy Sources
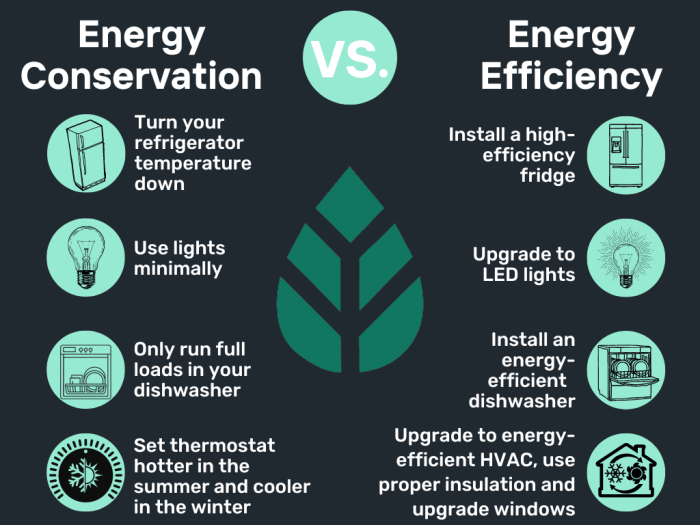
Renewable energy sources play a crucial role in enhancing energy efficiency by providing clean and sustainable alternatives to traditional fossil fuels. These sources are not only environmentally friendly but also contribute to reducing energy costs and increasing energy security.
Solar Energy
- Solar energy, derived from the sun, is one of the most abundant and widely available sources of renewable energy. It can be captured through solar panels and converted into electricity for residential, commercial, and industrial use.
- By harnessing solar energy, buildings can reduce their reliance on grid electricity, leading to lower utility bills and decreased carbon emissions.
- Case Study: The Empire State Building in New York City installed solar panels on its roof, significantly reducing its energy consumption and operating costs.
Wind Energy
- Wind energy is generated by harnessing the power of wind through wind turbines. It is a clean and renewable source of energy that can be used to generate electricity on both a small and large scale.
- Wind farms are being increasingly integrated into the energy mix to supplement traditional power sources and reduce carbon emissions.
- Case Study: The Hornsdale Wind Farm in Australia has successfully integrated wind energy into the grid, providing clean electricity to thousands of homes and businesses.
Geothermal Energy
- Geothermal energy utilizes heat from beneath the earth's surface to generate electricity and heat buildings. It is a reliable and sustainable source of energy that can help reduce reliance on non-renewable fuels.
- By tapping into geothermal energy, buildings can benefit from consistent heating and cooling solutions that are cost-effective and environmentally friendly.
- Case Study: The Oregon Institute of Technology campus in Klamath Falls, Oregon, uses geothermal energy for heating and cooling, reducing energy costs and carbon footprints.
Energy Efficiency Standards and Regulations

Energy efficiency standards and regulations play a crucial role in shaping the way energy is consumed and the impact it has on the environment. These regulations set guidelines for energy-efficient practices and technologies, aiming to reduce energy consumption and promote sustainability.
Key Energy Efficiency Standards and Regulations
Energy efficiency standards and regulations vary across different countries, each with its own set of guidelines and requirements. For example, the United States has established the Energy Star program, which sets energy efficiency standards for appliances and electronics. In the European Union, directives such as the Energy Performance of Buildings Directive set requirements for energy performance in buildings.
- The impact of these standards on energy consumption and environmental sustainability is significant. By setting minimum efficiency levels for products and buildings, energy consumption is reduced, leading to lower carbon emissions and overall environmental impact. These regulations also drive innovation in energy-efficient technologies and practices.
- Industries that have benefited from strict energy efficiency regulations include the automotive industry, where fuel efficiency standards have led to the development of hybrid and electric vehicles. The construction industry has also seen advancements in energy-efficient building materials and design practices due to building codes and regulations.
Closing Summary

In conclusion, energy efficiency is not just a buzzword but a crucial aspect of sustainable living. By implementing the strategies and standards discussed, we can pave the way for a greener future. Dive into the realm of energy efficiency and make a positive impact on our planet today.
Helpful Answers
What are some simple ways to improve energy efficiency in buildings?
Simple ways include using energy-efficient appliances, proper insulation, and energy-saving lighting.
How do renewable energy sources contribute to energy efficiency?
Renewable sources like solar and wind power create clean energy without depleting natural resources, thus enhancing energy efficiency.
Are there specific regulations for energy efficiency in commercial buildings?
Yes, many countries have regulations like minimum energy performance standards for commercial buildings to ensure energy efficiency.